A Quick Guide: How is a CNC Machine Programmed? | Rainhouse
A Quick Guide: How is a CNC Machine Programmed?
In the world of modern manufacturing, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines have transformed the way parts and components are fabricated with precision and efficiency. Behind the operation of these advanced machines lies a crucial process known as CNC programming. In this blog post, we will provide a quick guide on how a CNC machine is programmed, offering insights into the key elements and steps involved in the programming process. Whether you’re a machining professional, an aspiring programmer, or simply curious about CNC technology, this guide will help you understand the fundamentals of CNC machine programming.
CNC Programming Basics
The basics of CNC machine programming encompass the fundamental principles and techniques required to create precise instructions and codes that guide computer numerical control (CNC) machines in performing specific machining operations with accuracy and efficiency. The fundamental principles and techniques include:
Understanding G-code
- G-code serves as the language of CNC machines, providing instructions for precise control over their movements and operations. It enables machinists to program the machine’s actions, such as positioning, cutting, and tool changes, by using a series of commands.
- The syntax and structure of G-code commands follow a standardized format. Each command begins with a letter (typically G, M, or T), followed by a numerical code that represents a specific function or operation.
- Common G-code functions and parameters include tool movement, spindle control, coolant activation, tool changes, and dwell time.
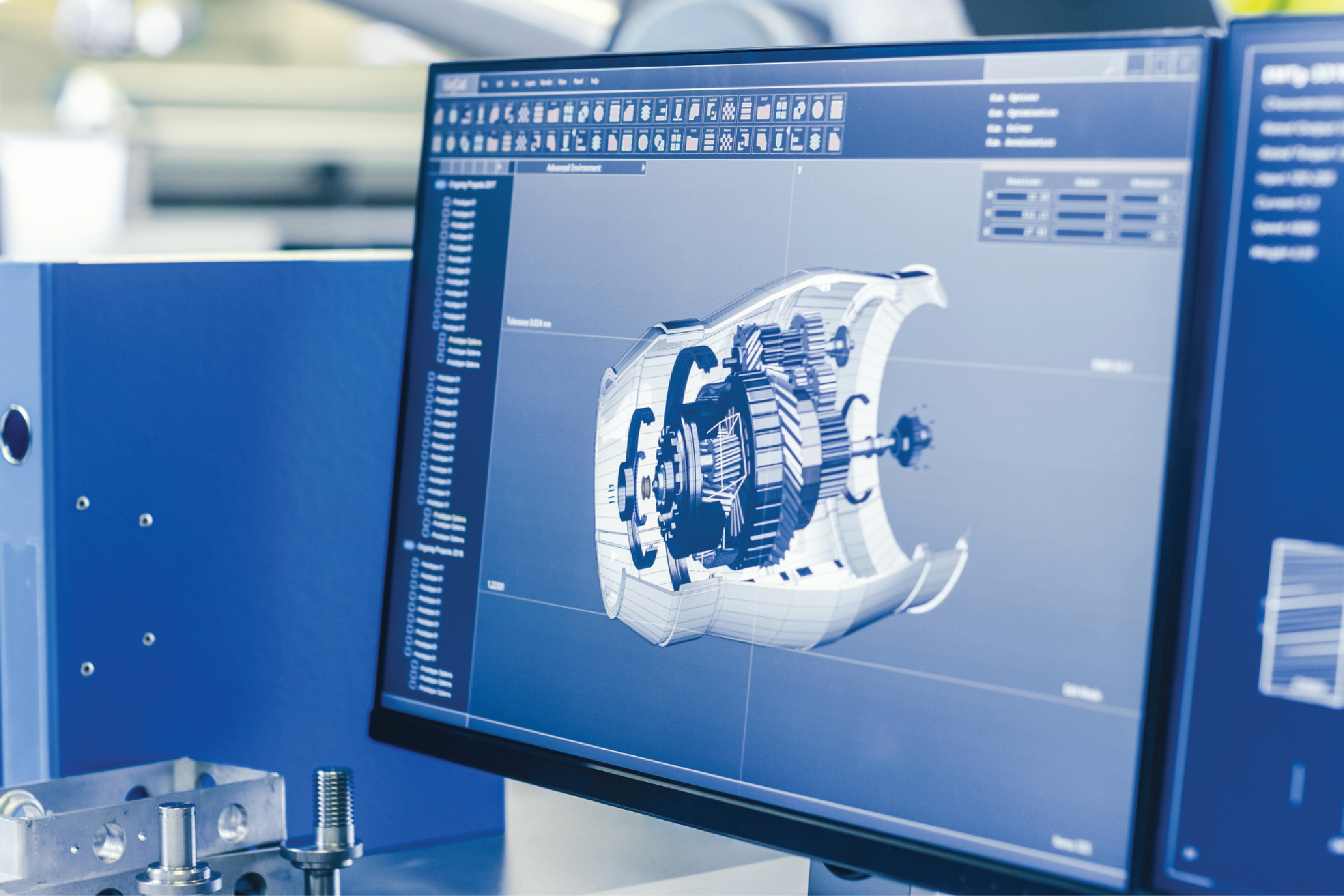
CAD/CAM Software
- CAD software serves as a digital design platform, allowing engineers, architects, and designers to create, modify, and optimize 2D or 3D models of products, structures, or components.
- CAM software, on the other hand, focuses on the manufacturing aspect of the design process. It takes the CAD model as input and generates instructions for the CNC machine to follow during the production phase.
- By utilizing CAM software, machinists can automate the generation of toolpaths, simulate machining operations, and perform collision detection to ensure safe and efficient production.
- To program a CNC machine using CAM software, CAD models need to be imported and prepared for machining. By importing CAD models into CAM software, machinists can prepare, simulate, optimize, and validate the machining process before executing it on the CNC machine.
Steps in CNC Machine Programming
The process of CNC machine programming involves a series of sequential steps. Here are some of the most common steps in CNC machine programming:
Designing the Part
- Creating a 3D model or 2D drawing in CAD software
- Defining geometric features, dimensions, and tolerances
Toolpath Generation
- Selecting appropriate cutting tools
- Defining toolpath strategies and parameters
- Simulating and optimizing toolpaths
Generating the CNC Program
- Translating the toolpath into G-code instructions
- Assigning feed rates, spindle speeds, and tool changes
- Post-processing the program for specific CNC machine compatibility
Programming Considerations and Techniques
When programming a CNC machine, there are various considerations and techniques that can enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and quality of the machining process. Some of the most common programming considerations and techniques include:
Workpiece Setup and Coordinate Systems
- Establishing the workpiece origin and coordinate system
- Defining tool offsets and tool length compensation
- Accounting for machine-specific coordinate systems
Tool Selection and Tooling Management
- Choosing the appropriate cutting tools for the job
- Defining tool parameters (diameter, length, geometry)
- Tool life monitoring and replacement strategies
Feeds and Speeds Optimization
- Determining optimal cutting parameters (feed rate, spindle speed)
- Considering material properties and cutting conditions
- Balancing productivity, tool life, and surface finish
Verifying and Simulating the Program
This is a critical step that involves using specialized software to check the code for errors, simulate the machining process, and ensure that the program will execute accurately and safely on the CNC machine. Verifying and simulating can be conducted through:
CNC Program Verification
- Performing a thorough program review for errors and inconsistencies
- Identifying potential collisions or tooling issues
- Utilizing software-based program verification tools
Virtual Machining Simulation
- Simulating the machining process virtually
- Identifying any potential issues or collisions
- Optimizing the program for efficiency and safety
Summary
CNC machine programming forms the foundation of modern manufacturing, allowing for precise control and automation of machining processes. Understanding the basics of CNC programming, including G-code language, CAD/CAM software, and the key steps involved, empowers manufacturers and programmers to unlock the full potential of CNC machines. By following a systematic approach to designing parts, generating toolpaths, and generating CNC programs, manufacturers can enhance productivity, accuracy, and efficiency in their machining operations. Stay updated with the latest advancements in CNC programming techniques and software to stay ahead in the dynamic world of CNC machining.
Rainhouse Manufacturing Canada Ltd.
At Rainhouse, we leverage the power of industry-leading software tools such as Autodesk: Fusion 360 to program our CNC machines. With Fusion 360’s advanced capabilities, we can seamlessly design parts, create toolpaths, and generate CNC programs with efficiency and precision. The software’s intuitive interface allows us to define part geometries, select appropriate tools, and optimize machining parameters to achieve optimal results. Additionally, Fusion 360’s integrated cloud-based platform enables seamless collaboration and version control among our team members, enhancing productivity and ensuring accurate program development. Furthermore, we utilize Fusion 360’s simulation features to verify and simulate the CNC machine programs, enabling us to detect any potential errors or collisions, optimize toolpaths, and ensure the safety and efficiency of the machining process. By harnessing the power of Autodesk: Fusion 360, Rainhouse Manufacturing Canada Ltd. maximizes programming efficiency and accuracy, ultimately delivering high-quality CNC machined parts to our valued clients.